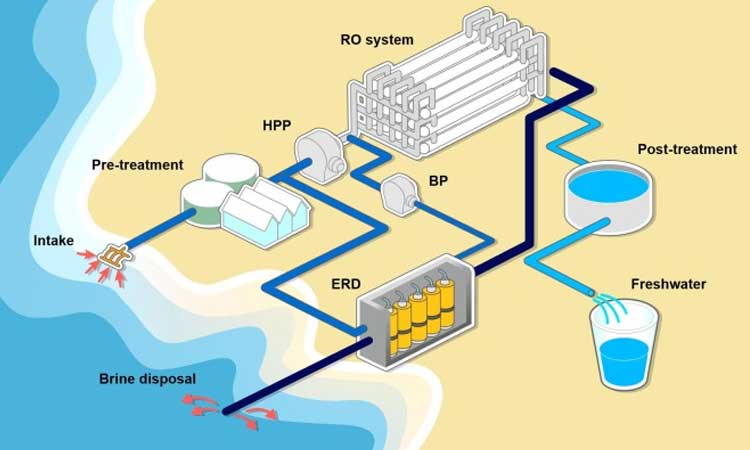
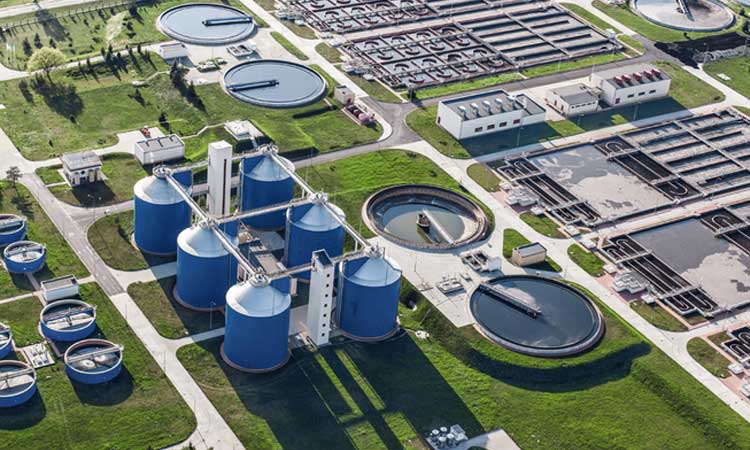
Lifecycle of water in a Desalination Plant
Seawater can not be used for human consumption because of the high salinity presented in the water. In this article, you will find how desalination methods lower the salinity levels of water. We will also be discussing all the ways of minimizing the salinity level of salty water. Also, the best method used for desalination of seawater.
Seawater contains high amounts of sodium, also known as saltwater. The water tastes very salty. The treatment of converting seawater or brackish water into potable water suitable for drinking is known as desalination.
Reverse Osmosis(RO) water purification systems are the best way to treat seawater. RO removes dissolved chemicals that are present in the water. For desalinating the salty water, other methods also include distillation, Freezing, Fresh evaporation, Hydrate formation, Electrodialysis.
Ten years ago, desalination was the crazy aunt in the attic. That's changed. It is now entering the mainstream and being taken seriously.- Barry Nelson
Ways of minimizing the salinity level of salty water are discussed below:
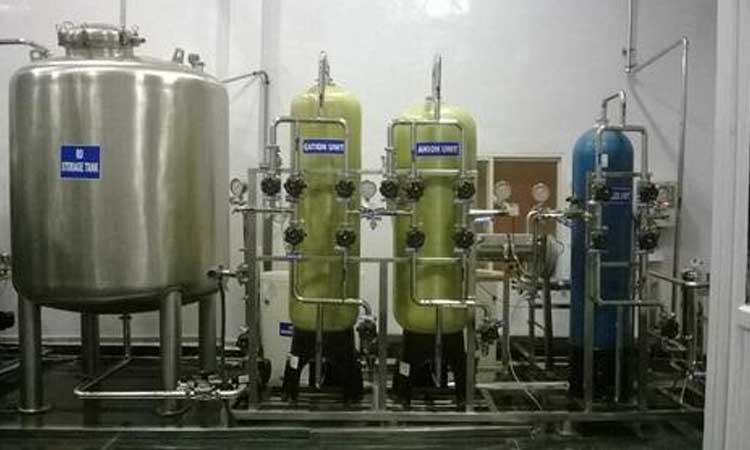
Reverse Osmosis (RO) water purification system: The reverse osmosis membranes used on desalination systems typically have a 99% salt rejection rate with a 45% recovery rate. The lower recovery rate is maintained to reduce the chances of scale formation within the desalination process.
Thermal Distillation: Water is heated at such a temperature that it evaporates, and after that, it condenses so that freshwater is obtained. The heat that we get from the condensation is also served to distill the water again. This desalination procedure is done in various stages by increasing and decreasing the temperature and pressure until freshwater is obtained.
Freezing: Freeze desalination involves three steps: ice formation, ice washing, and ice melting to obtain fresh water and subsequent removal of contaminants. An alternative physical process that can be used for desalting, based on the different freezing points of fresh and salt waters.
Flash Evaporation: An evaporation phenomenon caused by a sudden pressure drop sufficiently below the saturation pressure. Due to this sudden drop in pressure, the liquid undergoes a quick phase transition and the sensible heat of the liquid converts into latent heat of evaporation.
Hydrate formation: The hydrocarbons are added to the saline solution. It forms the complex crystalline hydrates that are separated later to obtain the desalinated water.
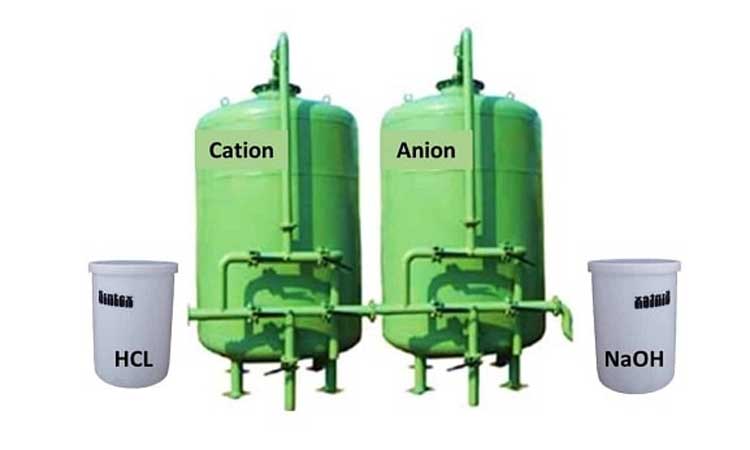
Electro Dialysis: The positive ions migrate towards negative ions, and the electric current is passed through the ion solution. Semipermeable membranes are placed between the electrodes. After this electrodialysis desalination process, the water obtained in the center of the electrolytic cell is desalinated, and freshwater is obtained.
The desalination of brackish water and seawater proves to be a reliable source of freshwater and is a solution for the world’s water shortage problem. Desalination processes normally produce drinking water in areas where only seawater or brackish water is the water source. Several technologies have been developed, and many more methods are under process for desalination.


















Comments
For states and big corporations, desal plants are in my eyes profitable, if they use free energy from renewable energy sources or just consume the energy overproduction (they would solve the energy storage problem).
The process is very energy intensive which is why, using reverse osmosis (RO) to produce high-quality water, the cheap availability of energy determines its commercial viability.
Actually it is quite difficult to desalinate sea water. The process is simple and well known but in practice it is not easy at all. There is a LOT of salt in sea water and whatever method you use, the salt residue builds up very fast and must be cleaned out frequently.