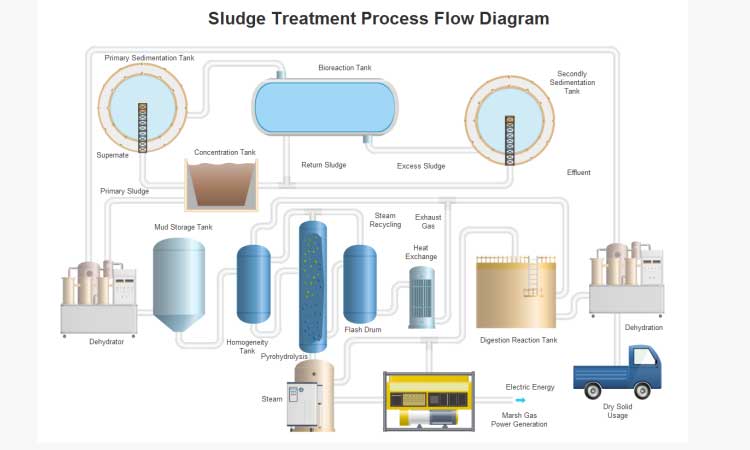
Sludge Treatment Process and its Different Stages
Two products are released as a by-product whenever the wastewater is treated. The first is the effluent, i.e., the treated wastewater, and the second is the sludge. This article first defines the sludge treatment, then the wastewater treatment process and at last, discusses the main steps involved in the sludge treatment process in sludge management.
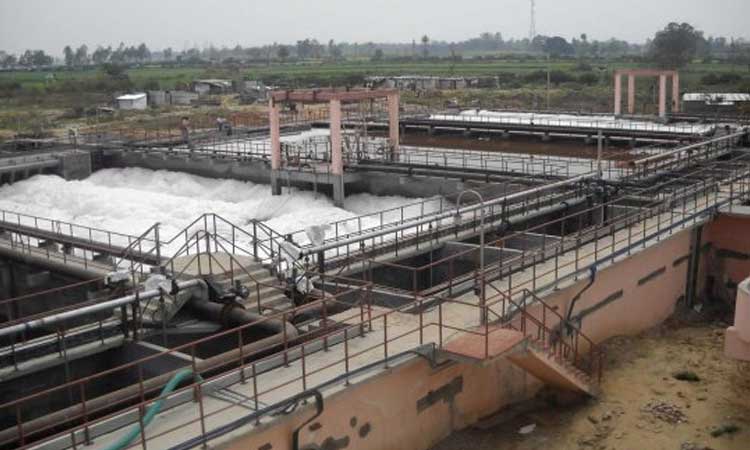
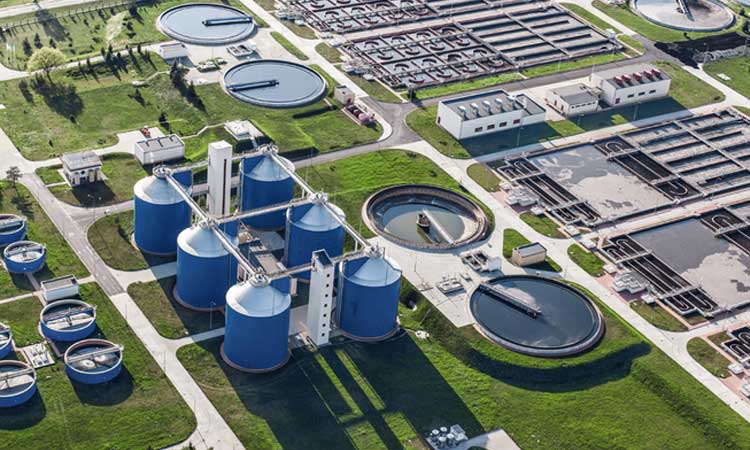
Sewage sludge is obtained from sewage treatment plants. The sludge consists of two primary forms, sludge and activated sludge. It contains many harmful substances such as dioxins and furans, polychlorinated biphenyls, and organochlorine pesticides. The range of processes is used to reduce or remove potential health risks. Also, remove water from sludge & reduce its weight and volume, thus reducing disposal costs.
If we move forward and don’t clean up the messes of the past, they’ll just get swept under the rug.- Erin Brokovich
The wastewater treatment is divided into four stages:
- Primary Wastewater Treatment Stage
- Secondary Wastewater Treatment Stage
- Tertiary Wastewater Treatment Stage
- Sludge Treatment
In pretreatment, large solids and grit are removed by screening. In primary treatment, the water is left to stand so that solids can sink to the bottom and oil and grease can rise to the surface. In secondary treatment, the sludge is further treated in sludge digesters. The tertiary treatment stage can remove up to 99 percent of the impurities from the wastewater. It produces effluent water that is close to drinking water quality.
In the stages mentioned above, the first three stages leave some settled solid particles known as sludge. The essential feature of sludge is that it contains a high amount of organic matter and moisture content. Because of the high amount of organic matter present, it is highly offensive and, if disposed of untreated into the environment, may cause damage to it.
Stages involved in sludge treatment are discussed below:
Sludge Thickening: The first stage in the treatment process aims to reduce the moisture content. It becomes indispensable to reduce the amount of water content in sludge and thicken it.
Sludge Digestion: Decompose the organic matter present inside the sludge. Sludge digester-A treatment system used for sludge digestion. It can do it through either aerobic processes or anaerobic processes.
Conditioning: It enables to enhance the performance of sludge or to make sludge capable of dewatering. It is done with the help of chemical conditioners.
Sludge Dewatering: In the thickening process, the moisture content will reduce up to 90%, which will be done using the sludge dewatering process.
Heat Drying: The sludge that is produced after the sludge dewatering treatment is treated. It is used to reduce the moisture content that will be released in gas form. This gas produced helps maintain the wastewater treatment plants.
Incineration: At the present process, the sludge has very little moisture content and organic matter. Therefore it will be elementary to incinerate.
An alternative for the stabilization and ultimate disposal of wastewater sludge is composting. It is a type of aerobic digestion. Sewage sludge can be combined with other waste materials before composting to provide a pasteurized product. Thus, the process can achieve waste treatment with resource recovery and represents a beneficial use of sludge. The advancements have increased the use of the process for wastewater sludge management. With these practices, wastewater treatment facilities can produce a safe compost of consistently good quality in an environmentally sound manner.

















Comments
Sludge is recycled to make products intended for sale in the marketplace. Such components/ products may be bio-soils (mixture of sludge with other materials), energy (bio-gas, electricity, oil, heat etc.), nutrients (phosphate, nitrogen), metals (coagulants) etc.
Once the volatile solids are fully consumed the remaining ash must be physically removed and disposed of by hauling it to a landfill or taking it to a plant for further processing like composting.
The sludge is treated biologically and chemically to remove BOD, TSS, NH3, PO4 metals etc. There are microscopic organisms that break down the sludge and in some cases, the sludge is taken and used to manufacture fertilizer.