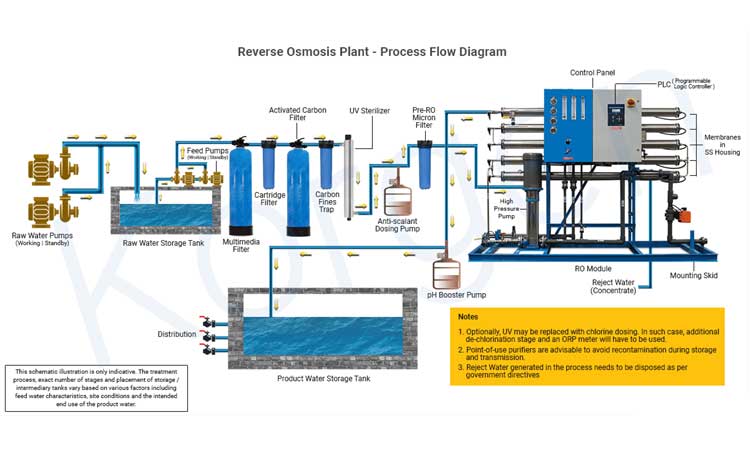
Technology and Tools Work Behind the RO Plant System
Reverse Osmosis is a technology used to remove contaminants from water by pushing the water under pressure through a semipermeable membrane. This article covers the understanding of Osmosis and Reverse Osmosis Water, workings of RO, and the tools used in RO. It aims towards an audience with little or no experience with Reverse Osmosis water. It will attempt to explain the basics in simple terms that should give the reader a better overall understanding of Reverse Osmosis water technology and its applications.
Osmosis is a naturally occurring phenomenon and one of the essential processes in nature. It is a process where a weaker saline solution will tend to migrate to a robust saline solution. When a cell is submerged in water, the water molecules pass through the cell membrane from an area of low solute concentration to high solute concentration. (explained in the diagram)
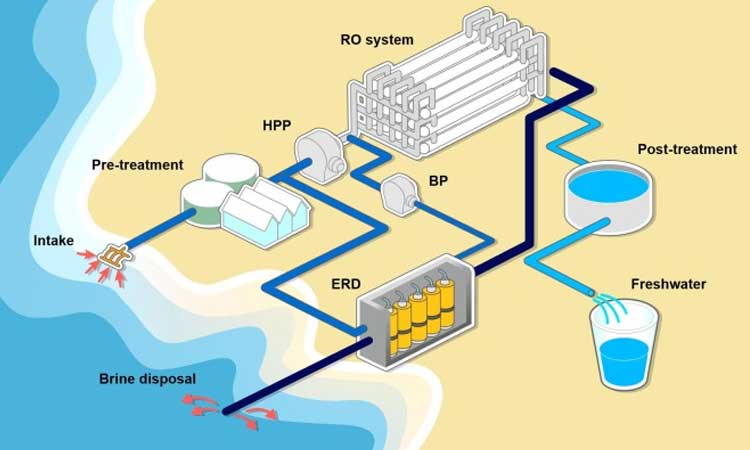
Reverse Osmosis is the process of Osmosis in reverse. Whereas Osmosis occurs naturally without the energy required. To reverse the process of Osmosis, we need to apply power to the more saline solution. A reverse osmosis membrane is a semi-permeable membrane that allows the passage of water molecules but not the majority of dissolved salts, organics, bacteria, and pyrogens (diagram shows the process of reverse osmosis).
Caring for water is caring for us all.- The Dharma Trails
Workings of RO
Reverse Osmosis works by using a high-pressure pump to increase the pressure on the salt side of the RO and force the water across the semipermeable RO membrane, leaving almost all (around 95% to 99%) of dissolved salts behind in the reject stream. It is important to understand that an RO system employs cross filtration rather than standard filtration, where the contaminants are collected within the filter media. With cross filtration, the solution passes through the filter or crosses the filter with two outlets: the filtered water goes one way, and the contaminated water goes another way.
Saving in Capital and Operating expense of treatment plant. A CETP is said to be more reliable when the values of pollutants in the effluent treated by the plant. And meet the set discharge standards more often than those of a CETP that frequently exceeds the standards. Regular treatment is constantly less expensive than small-scattered treatment units. Land availability is hard to guarantee by all individual units if they go for individual treatment plants. Industry Water Solutions provides you with a one-stop solution for wastewater treatment methods. Don't hesitate to get in touch with us for more details.
Removal of Contaminants
Reverse Osmosis can remove up to 99%+ of the dissolved salts (ions), particles, colloids, organics, bacteria, and pyrogens from the feed water. An RO membrane rejects contaminants based on their size and charge. Reverse Osmosis effectively treats brackish, surface, and groundwater for both large and small flows applications. Some examples of industries that use RO water include pharmaceutical, boiler feed water, food and beverage, metal finishing, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Membrane Cleaning
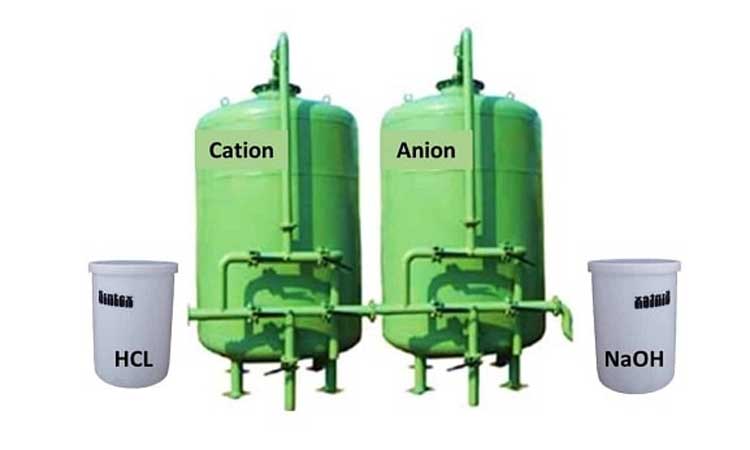
Depending on the feed water quality, RO membranes will inevitably require periodic cleaning, anywhere from 1 to 4 times a year. As a general rule, if the normalized pressure drop or the normalized salt passage has increased by 15%, it is time to clean the RO membranes. If the normalized permeate flow has decreased by 15%, it is also time to clean the RO membranes. RO membrane cleaning involves low and high pH cleaners to remove contaminants from the membrane.
As the water temperature decreases, the RO membrane becomes more viscous, and the RO permeate flow will drop as it requires more pressure to push the water through the membrane. Likewise, when the water temperature increases, the RO permeate flow will increase. As a result, performance data for an RO system must be normalized, so those flow variations are not interpreted as abnormal when no problem exists.
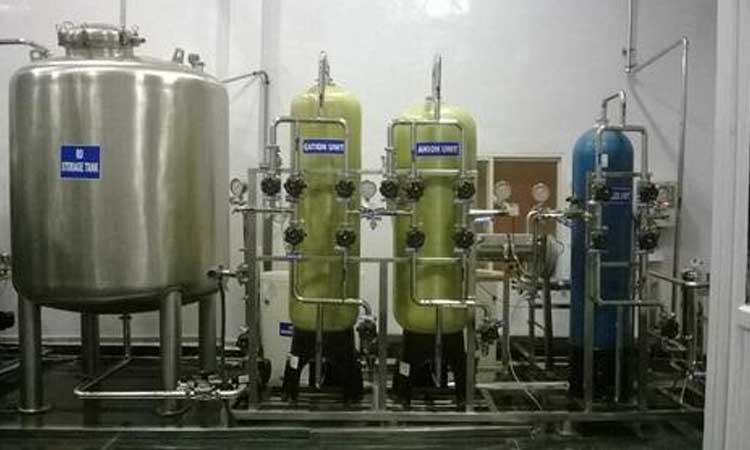
Storage Tank, Automatic Shut-off Valve (SOV), Check Valve, Cold Water Line Valve, Drain Line, Flow Restrictor, Pre-filter, Carbon Filter, Post-filter, RO Faucet, RO Membrane these are some of the tools used in Reverse Osmosis to purify the water.
From my point of view, Reverse Osmosis is an effective and proven technology to produce water suitable for many industrial applications requiring demineralized or deionized water. Further post-treatment after the RO system, such as mixed bed deionization, can increase the quality of the RO permeate and make it suitable for the most demanding applications. Proper pretreatment and monitoring of an RO system are crucial to preventing costly repairs and unscheduled maintenance. With the correct system design, maintenance program, and professional service support, RO system should provide many years of high purity water.

















Comments
We have lost such resources either by acquiring this land for staying purpose or by ignoring them and making them dirty, so unable to use water even for use.
Water resources are sources of water that are useful or potentially useful to humans and are important because it is needed for life to exist.Many uses of water include agricultural, industrial, household, recreational and environmental activities.
An atmospheric water generator (AWG) is a device that extracts water from humid ambient air. Water vapor in the air is condensed by cooling the air below its dew point, exposing the air to desiccants, or pressurizing the air.